222. 完全二叉树的节点个数 Easy
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层(从第 0 层开始),则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
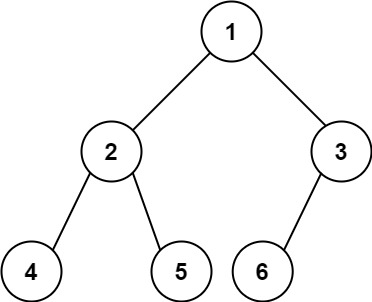
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
解题思路
输入: 一个完全二叉树的根节点 root。
输出: 要求在时间复杂度低于 O(n) 的情况下计算出树的节点个数
本题属于遍历二叉树问题。
我们可以利用“完全二叉树”的结构特性把复杂度从 O(n) 降到 O((log n)^2):
- 若一棵树的左高(一路往左的深度)等于右高(一路往右的深度),说明它是满二叉树,节点数直接是
2^h - 1。 - 否则就不是满的,递归统计:
1 + 左子树节点数 + 右子树节点数。
因为完全二叉树保证了子树要么是满的,要么仍是完全的,因此每层都能用“是否满树”的快速判断来剪枝。
代码实现
python
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
# 定义计算左子树高度的函数
def leftHeight(node):
h = 0 # 初始化高度为0
while node: # 沿着左子节点一直向下
h += 1 # 高度加1
node = node.left
return h # 返回左子树高度
# 定义计算右子树高度的函数
def rightHeight(node):
h = 0 # 初始化高度为0
while node: # 沿着右子节点一直向下
h += 1 # 高度加1
node = node.right
return h # 返回右子树高度
# 计算当前树的左子树和右子树高度
lh = leftHeight(root)
rh = rightHeight(root)
# 如果左子树高度等于右子树高度,说明是完美二叉树
if lh == rh:
return 2 ** lh - 1 # 完美二叉树的节点数公式:2^高度 - 1
# 如果不是完美二叉树,递归计算左右子树的节点数并加上根节点
return 1 + self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right)javascript
var countNodes = function(root) {
function leftHeight(node) {
let h = 0;
while (node) {
h ++;
node = node.left;
}
return h;
}
function rightHeight(node) {
let h = 0;
while (node) {
h ++;
node = node.right;
}
return h;
}
const lh = leftHeight(root);
const rh = rightHeight(root);
if (lh === rh) return 2 ** lh - 1;
return 1 + countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right);
};复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O((log n)^2)
空间复杂度:O(logn)